Early detection of vascular diseases has never been more important. Cardiovascular diseases remain the leading cause of death worldwide, with Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) being one of the most frequently overlooked risk factors. The Ankle-Brachial Index (ABI) provides a solid foundation for assessing peripheral artery disease (PAD), while complementary parameters such as the Pulse Wave Index (PWI™) can help identify earlier vascular changes.
Why ABI Matters
ABI measurement is a fast, non-invasive way to assess arterial blood flow and identify any hidden vascular issues. Its clinical benefits are clear:
- early identification of cardiovascular risk
- improved treatment strategies
- detection of silent (asymptomatic) PAD
- increased patient engagement
- high diagnostic value at low cost
When the ABI is low, it clearly signals a substantially increased cardiovascular risk. Moreover, research shows that these patients can be up to six times more likely to experience heart attacks, strokes, or other major events.
Limitations of Manual ABI Testing
Traditional ABI measurement using a handheld Doppler device requires training, time, and experience. It is important to note that results often vary between operators, which makes consistent PAD screening difficult in everyday practice despite strong guideline recommendations.
User-dependent:
The test must be performed by well-trained personnel who can accurately locate and identify the correct arteries while detecting even the slightest blood flow signals.
Lengthy process:
Manually measuring pressure values at all relevant arteries can take up to 15 minutes per patient.
No side comparison:
Because measurements are not taken simultaneously, small differences in blood flow between the patient’s left and right limbs cannot be documented.
Not suitable for diabetic patients:
The method is not reliable for patients with medial sclerosis, a condition commonly found in individuals with diabetes.
How Automated ABI Systems Improve Diagnostics
Modern automated ABI technology addresses these challenges by providing standardised, simultaneous measurements. This reduces operator dependency and improves accuracy, allowing ABI testing to become a routine part of clinical workflows and screening programmes.
Such multiparameter systems, which combine ABI with additional indices such as the Pulse Wave Index (PWI™) or Toe-Brachial Index (TBI), not only improve efficiency, but also provide deeper diagnostic insight. They enable clinicians to detect vascular changes at an earlier stage, thereby improving preventive care and patient outcomes.
AngE™ ABI+ by SOT Medical Systems
A leading solution in this field is the AngE™ ABI+ system, developed and manufactured in Austria according to ISO 13485:2016 standards. This innovative platform integrates multiple vascular diagnostic tests into a unified system, offering a comprehensive and streamlined approach to healthcare.
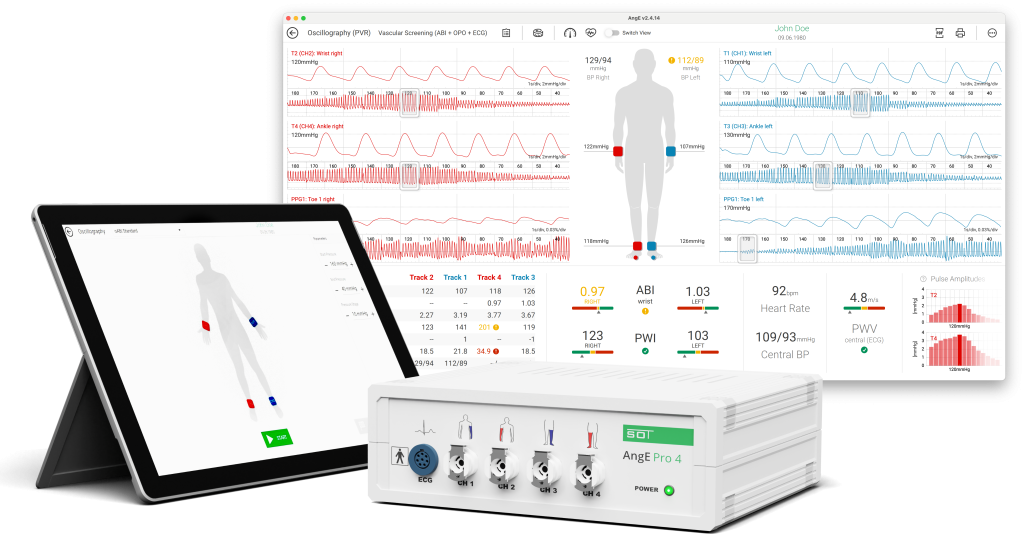
- ABI (Ankle-Brachial Index)
- The TBI (toe-brachial index) is a measurement used to assess the health of patients with diabetes.
- Pulse Wave Index (PWI™) is an advanced vascular analysis tool for early detection of (often asymptomatic) PAD
AngE™ ABI+ is a trusted solution that has been installed in thousands of locations worldwide, including general practitioner offices, vascular clinics and hospitals.
A reliable tool for an ageing population.
As the prevalence of diabetes and cardiovascular disease rises, the importance of early detection of peripheral artery disease (PAD) increases. Automated systems such as AngE™ ABI+ deliver quick, reliable, and reproducible ABI measurements with minimal training.
Early detection is key to saving lives. Automated ABI technology facilitates this process.
👉 Learn more here

